All Textbook Topics - Electricity - Current in series and parallel circuits - In a parallel circuit, the current going out and into the battery is equal to the sum of the current in each of the branches
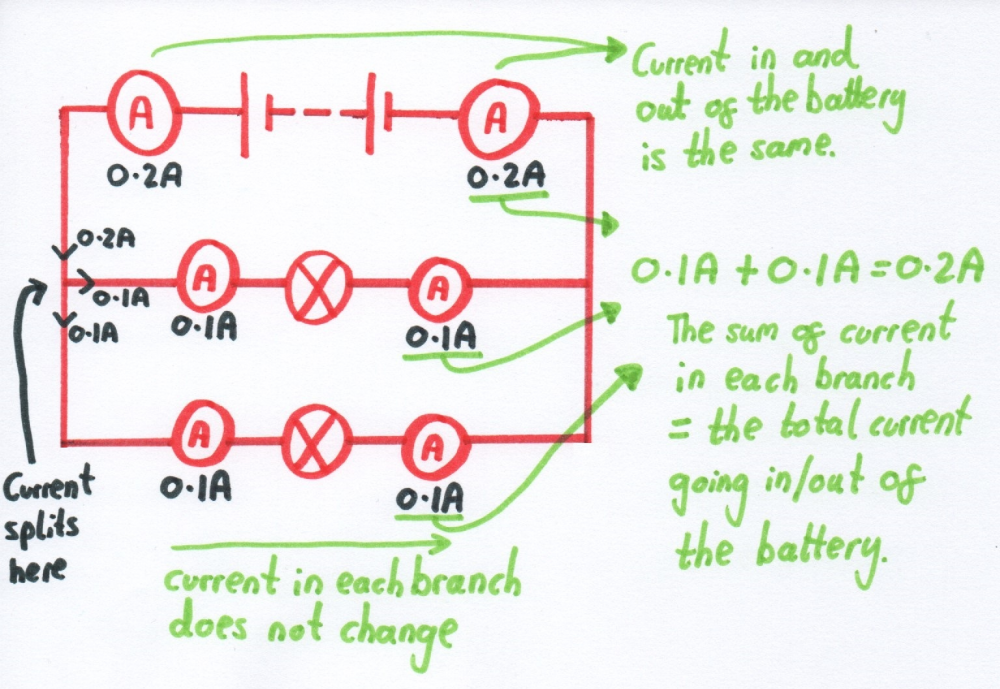
In a parallel circuit, the current going out and into the battery is equal to the sum of the current in each of the branches
In a parallel circuit, to calculate the total current coming out of the battery, you must add up the current in each parallel branch.
You must calculate it like this or you will get the wrong answer.
The amount of current that goes down each branch depends on the resistance of the branch. A higher resistance (e.g. more bulbs) in the branch means a lower current in that branch.
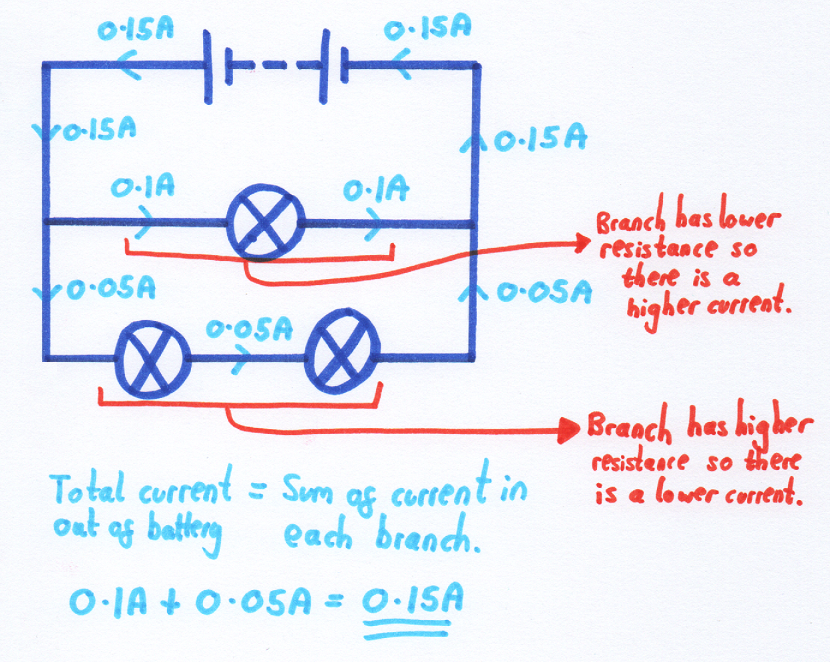
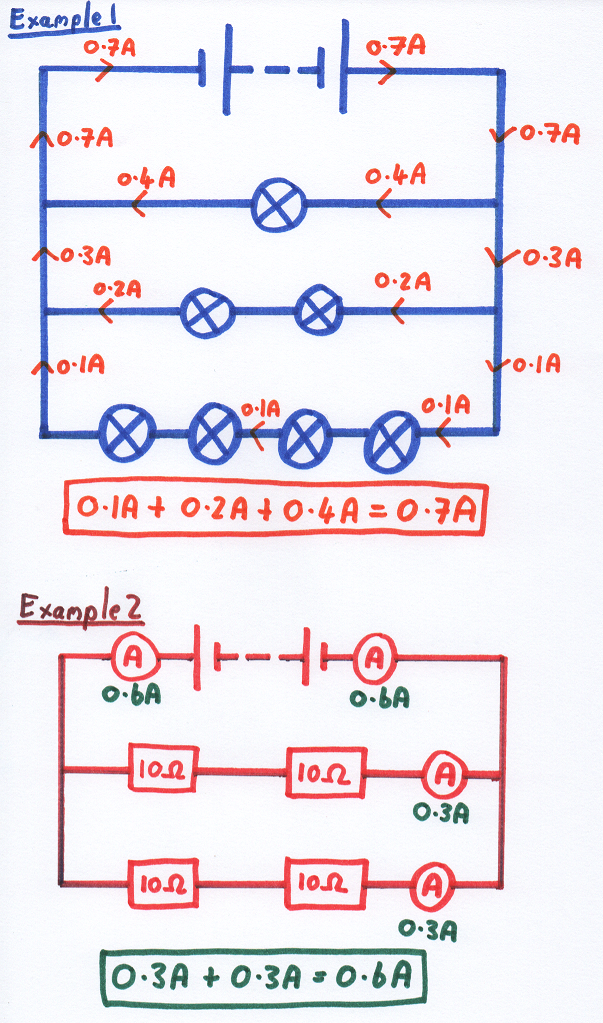
The total current out/in to the battery is equal to the sum of the currents in each branch. Here are some more examples of this in action:
All of our textbook pages have associated quizzes. Register for free to access them.
Register For Free