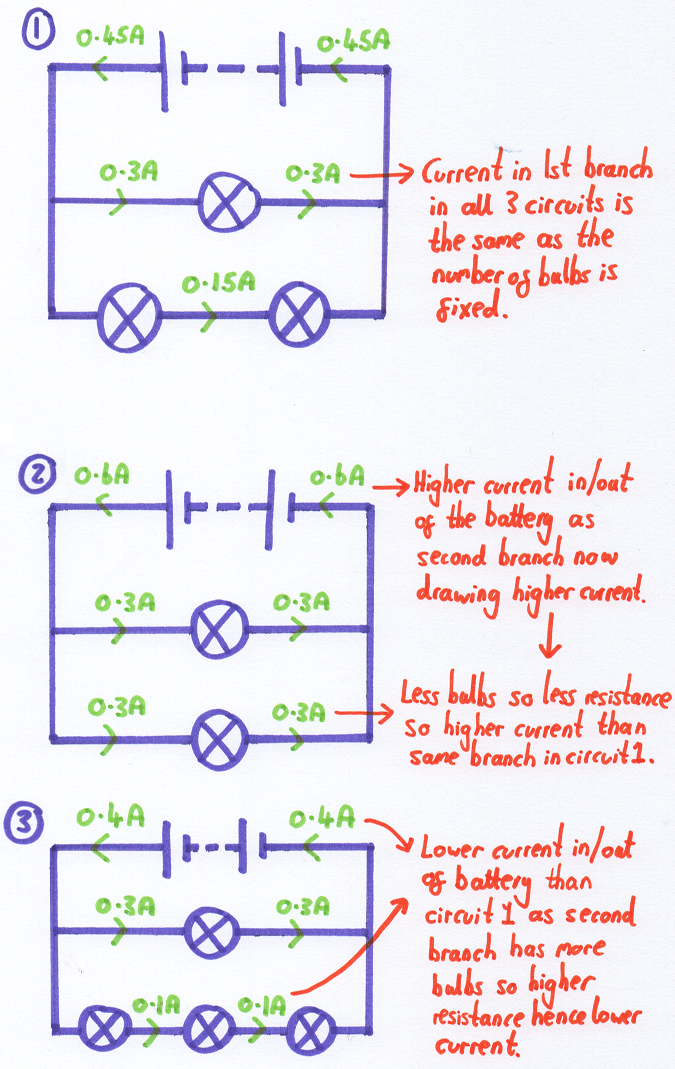
All Textbook Topics - Electricity - Current in series and parallel circuits - When you change the resistance (number of bulbs) in a parallel branch, you change the current in that branch and the total current going in and out of the battery only. The current in the other branches is not affected.
When you change the resistance (number of bulbs) in a parallel branch, you change the current in that branch and the total current going in and out of the battery only. The current in the other branches is not affected.
In parallel circuits, each parallel branch operates independently.
In the example of three circuits below:
- The first branch has the same bulb and battery pack in each one, so the current in each of the first branches is constant.
- The current in the second branch changes as the number of bulbs, and hence the resistance in the second branch changes.
- As the current in the second branch changes, so does the total current out/in to the battery
- When the resistance in the second branch increases, the current goes down.
- When the resistance in the second branch goes down, the current goes up.
All of our textbook pages have associated quizzes. Register for free to access them.
Register For Free