All Textbook Topics - Forces introduction - Types of forces - The normal reaction force occurs as an equal and opposite reaction force to an applied force on a stable object
The normal reaction force occurs as an equal and opposite reaction force to an applied force on a stable object
When you push against a stable object, assuming that the surface does not give-way or move, the surface pushes back with an equal and opposite force. This equal and opposite force is called the normal reaction force. This happens when you place objects on a surface, like this box on a table:
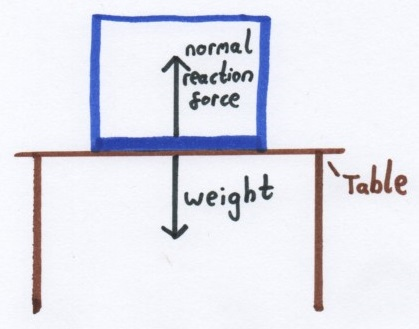
It also happens when you push horizontally against a surface, a wall for example. The normal reaction force must be equal and opposite to the pushing force:

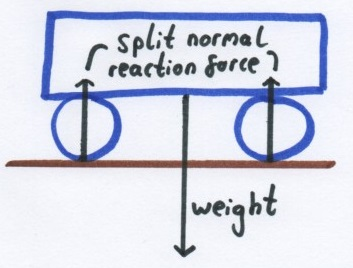
If an object has multiple points of contact then the normal reaction force will be split between these. The total magnitude of all the normal reaction forces must equal the original pushing force.
For example, the two normal reaction forces in the diagram of the trolley below are equal to the weight of the trolley.
All of our textbook pages have associated quizzes. Register for free to access them.
Register For Free